Transistors, the building blocks of modern electronics, have revolutionized our daily lives. Two popular types of transistors - the NPN (Negative-Positive-Negative) and PNP (Positive-Negative-Positive) - are widely utilized in electronic circuits. In this article, we will delve into the differences between NPN and PNP transistors, explore easy methods of identification.
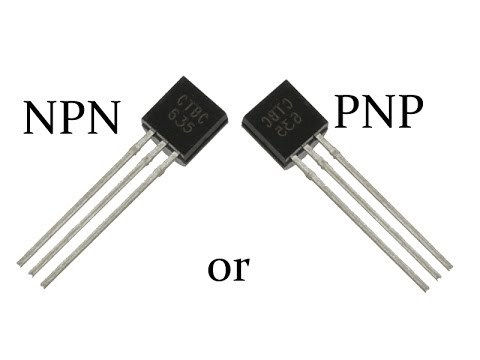
Difference Between NPN and PNP Transistors:
At the core, NPN and PNP transistors are both bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) with a similar basic structure. However, they differ in the arrangement of P-type and N-type semiconductor materials. In an NPN transistor, one P-type semiconductor is sandwiched between two N-type semiconductors, while a PNP transistor comprises one N-type semiconductor between two P-type semiconductors.
The fundamental difference between these transistors lies in their mode of operation. For an NPN transistor, a small current flowing from the base to the emitter allows a larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter. Conversely, in a PNP transistor, a small current leaving the base permits a larger current to flow from the emitter to the collector.
Distinguishing NPN and PNP Transistors:
An easy way to tell NPN and PNP transistors apart is to examine the arrow marked on each transistor's symbol. The arrow will point inwards towards the base for NPN transistors and outwards from the base for PNP transistors.
Another method involves using a multimeter to confirm the transistor's type. Set the multimeter to diode mode, and if the highest resistance is obtained when the positive lead is connected to the base and the negative lead is connected to the emitter, the transistor is NPN. Similarly, if the highest resistance is achieved when the negative lead is connected to the base and the positive lead is connected to the emitter, you have a PNP transistor.
Application of NPN and PNP Transistors:
Both NPN and PNP transistors find widespread use in various electronic applications. The NPN transistor is considered the default choice for general-purpose switching and amplification due to its faster response time and high efficiency. Some common applications include digital logic circuits, audio amplifier stages, and power supplies.
PNP transistors, on the other hand, are often used in combination with NPN transistors for complementary or push-pull configurations. This approach significantly reduces both noise and distortion, making it a popular choice for audio amplifiers and power output stages.
Understanding the differences, identification methods, and applications of NPN and PNP transistors is crucial for anyone interested in the field of electronics. By learning about these essential components, you will be better equipped to design and troubleshoot a wide range of electronic devices. Keep exploring and experimenting with these fascinating little gems that have transformed the world of technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a NPN transistor made of?
The npn transistor is made up of three semiconductor layers: one p-type semiconductor layer and two n-type semiconductor layers. The p-type semiconductor layer is sandwiched between two n-type semiconductor layers. The npn transistor has three terminals: emitter, base and collector.
How does an NPN transistor work?
The NPN transistor is designed to pass electrons from the emitter to the collector (so conventional current flows from collector to emitter). The emitter "emits" electrons into the base, which controls the number of electrons the emitter emits.
Can I use NPN instead of PNP?
NPN and PNP transistors are interchangeable if you remember one simple rule: A bipolar transistor is essentially two back-to-back diodes with the base being the common connection.
Products Category