Since the sampling resistor is on the high side, the current in this method is very different from that on the low side, so the low side method cannot be used.
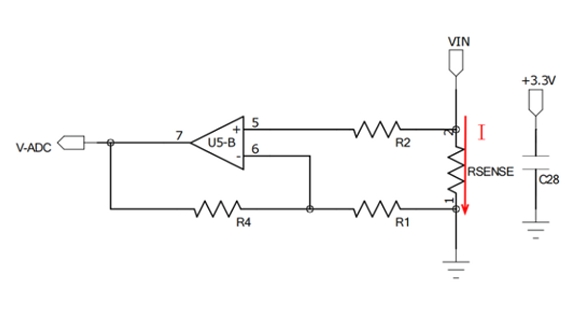
Figure 1 Traditional low-side current sampling method
Therefore, it is necessary to reconstruct the power supply voltage (VCC, whose reference ground is VOUT) for the op amp, which is achieved through the op amp + transistor method.
method one:
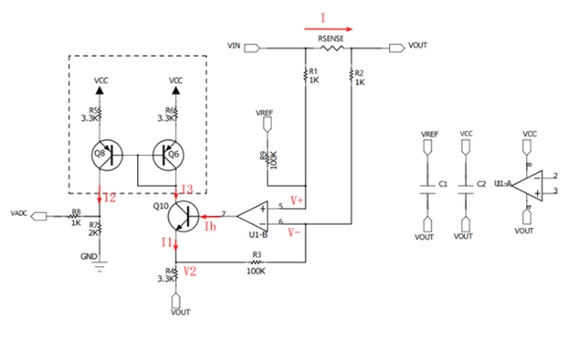
Figure 2 Op amp + NPN mode
Analysis process:
①The dotted frame position in the above figure is a current mirror circuit composed of two transistors of the same type, so it can be concluded that I2=I3;
② From the triode Q10, we can get I1=I3+Ib≈I3 (due to the triode amplification factor β>>1), that is, I1=I2;
③From the virtual break of the op amp, we can get: V-=V2*R2/(R3+R2);
④ From the virtual short of the op amp, we can get: V-=V+;
⑤According to Kirchhoff’s current law: (Vref - V+)/R9 = (V+ - Vin)/R1;
==> V+ = (Vref + Vin*R9/R1) / (1+R9/R1)
⑥Assume R1=R2, R3=R9;
⑦ From the above, it can be concluded that VADC=(R9*Vin/R1+Vref)*R7/R4
⑧Vin= I *Rsense into the above formula, we can get
VADC=(R9*I *Rsense/R1+Vref)*R7/R4
⑨The introduction of Vref is a voltage reference added to eliminate the static deviation of the op amp.
Method two:
.png)
Analysis process:
① Since the op amp input bias current I3 I4 is very small and can be ignored
② From the transistor Q11, we can get: I1=I2+Ib is approximately equal to I2;
③ If the op amp has a virtual break, it can be obtained: V+= Vref * R2/(R2+R3);
④It can be obtained from the virtual short of the op amp: V+=V-
⑤I1=(Vin - V-)/R1 , Vin=I*Rs1
⑥It can be concluded from the above
Vadc=I*Rs1*R4/R1-Vref*R2*R4/(R1*(R2+R3))
Vref is a negative value, which can eliminate the error caused by the offset voltage of the op amp.

