DC-DC converters play a vital role in areas such as electric vehicles, transportation systems, and renewable energy microgrids. This article classifies DC-DC converters and discusses their advantages and limitations. In addition, the article also introduces an improved DC-DC converter topology that combines Cuk and Positive Output Super Slow (POSLL) topology to achieve higher voltage gain with fewer components.
DC-DC converters are mainly divided into two topologies: isolated and non-isolated. Isolated converters separate the load from the input source through a high-frequency transformer and are suitable for scenarios where sensitive loads need to be protected. However, isolated converters also have some problems, such as EMI noise, energy recovery circuit requirements, increased losses, etc.
In contrast, non-isolated converters do not require isolation of the input source and load and are suitable for most applications such as high-intensity discharge lamps and renewable energy systems. This article also describes traditional non-isolated DC-DC converter types capable of boosting the input voltage, including boost, buck-boost, Cook and SEPIC topologies.
However, conventional converters have some limitations in providing high voltage gain. To solve this problem, the article proposes a Positive Output Super-Low (POSLL) converter, which achieves greater voltage gain by using a smaller duty cycle percentage. POSLL converters can achieve voltage gains of up to 3 as the duty cycle approaches 50%, compared to traditional topologies that typically have voltage gains of 1 or 2.
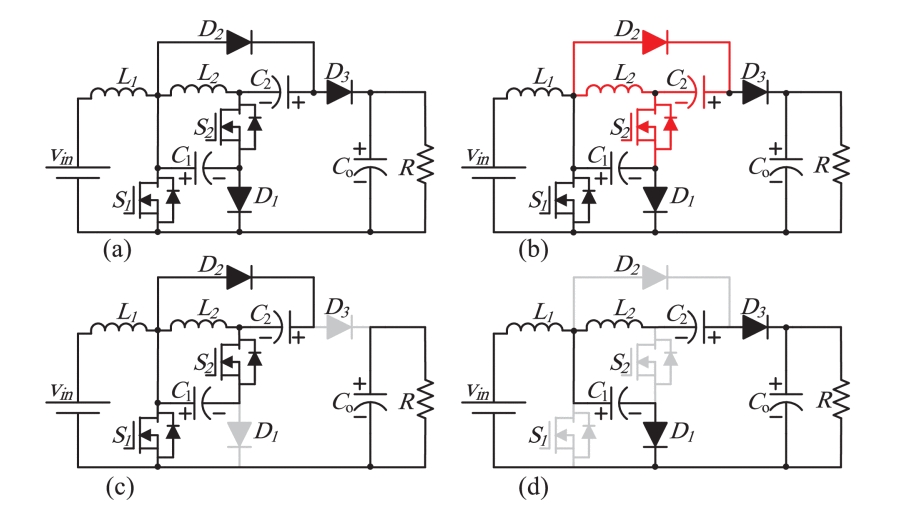
Fig. 1: The proposed converter topology Source: IEEE Access
In order to further increase the voltage gain and improve efficiency, this article proposes an improved secondary DC-DC converter topology that combines Cuk and POSLL topologies. The topology design is simple and includes two inductors, three capacitors, three diodes and two switches. With this combination, the topology achieves higher voltage gain and reduces component count.
In summary, this article explores the classification, advantages and disadvantages of DC-DC converters, and proposes a new improved topology to improve voltage gain and efficiency. This innovative topology is expected to develop in areas such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.

